Wheat grains are a product unique in nature. They are able to maintain beneficial properties to a sufficient extent for a quarter century. Of course, today there is no need to store the crop for such a long time, however, even until the next season, wheat may not last if it is not clearly observed the proper storage conditions for grain.
Wheat storage rules
Wheat is very demanding on storage conditions. There are standard norms that allow you to keep the crop for more than a year. So, the permissible moisture content of stored grain should not exceed 14%. At the same time, the storage temperature should be within + 10 ... + 15 ° С.
Did you know? The first elevator was built in 1845 in the United States.
Before you send the crop to the store, you should carefully check it for the presence of harmful microorganisms and pest larvae. If molds, pathogens or insects are found, you need to treat the crop with specialized drugs.
 In order for the temperature and humidity indicators in the granary to remain at the proper level throughout the entire storage period, it is necessary to periodically dry the mass, ventilate and cool if necessary, which is not as difficult in modern technology as it was several decades ago.
In order for the temperature and humidity indicators in the granary to remain at the proper level throughout the entire storage period, it is necessary to periodically dry the mass, ventilate and cool if necessary, which is not as difficult in modern technology as it was several decades ago.
Special rooms
Granaries are used to store cereal seeds. In small farms, the premises in which the crop is stored are most often constructed from available materials.
The most popular of them are:
- metal;
- brick;
- reinforced concrete.
Did you know? The largest elevator in Russia is located in the Voronezh region. The complex is simultaneously capable of containing 300 thousand tons of grain.
Whatever material the building is built from, it must meet the following requirements:
- Strength. Walls must withstand the pressure of the wheat mass.
- The absence of any odors.
- Dryness. A granary cannot be built in places where groundwater is located close to the surface, and also on the banks of rivers, ponds and lakes.
- Tightness. Harvest must be protected from rain.
- Smooth wall and floor structureto exclude the development in the gaps of pathogens.
- Humidity.
- Ventilation. The ventilation hole should close tightly if necessary.
- Wood flooring. Harvest can not be stored on concrete or stone floor.
- Disinfection. Before laying the crop, the granary should be treated with formalin vapor or sulfur dioxide.
Among other things, to monitor the condition of the grain and, if necessary, mix it, the granary should be equipped with special wooden flooring.

Large quantities of grain are stored in elevators, which are highly mechanized storage. Unlike conventional granaries, an elevator is a whole complex for receiving and storing crops.
As a rule, they include:
- working building;
- silos;
- automatic device for receiving and pouring wheat;
- equipment for drying seeds;
- weight, etc.

Storage tanks
Everywhere, special containers are used to store wheat. They are sealed structures, allowing full control over the quality of stored grain.
Tanks for storing cereals are of the following types:
- Ground. These prefabricated metal structures are designed for large crop volumes. However, storing wheat in them for a long time will not work, because such structures are poorly protected from rain and pests.
- Grain silos. Cylindrical structures are flat-bottomed and conical. Cone silos are used for temporary storage of both dry and wet seeds. Flat-bottomed structures, due to complete tightness, are designed for long-term storage of cereal crops. Such designs are equipped with a thermal control system, which automatically controls the level of humidity and temperature, which ensures the validity of the crop.
- Reinforced concrete. As a rule, such containers are cylindrical or similar to a one-story building. By their characteristics, they are inferior to silos, because they do not provide complete protection against rodents and parasites. In addition, the construction of such structures is unreasonably costly.
Wheat Storage Methods
The storage method for feed, spring and winter wheat depends on the quality of the grain and the volume of the crop. There are two ways to store cereals - in bulk and in bags. As practice shows, a more convenient and more frequently used method is bulk storage. Indeed, in this way, the volume of the granary is used as efficiently as possible, in addition, the crop is convenient for transportation, as well as for monitoring its condition. Also, storing grain in bulk allows you to significantly save on packaging.

Dry
The dry method for storing grain is often used. It involves extracting the maximum possible amount of moisture from the seeds. With the dry method, the bacteria located on the surface of the cereal cease to multiply and fall into suspended animation. But there remains the danger of damage to the seeds by rodents or insects.
Grain dehydration occurs in two ways:
- natural;
- using thermal equipment.
 The most beneficial drying method is to process the crop with fresh air and sunlight and heat.
The most beneficial drying method is to process the crop with fresh air and sunlight and heat.
The safest, in every sense, is the airless method or the conservation of wheat. With this method, the grain retains its beneficial properties as much as possible, and without oxygen, most of the microorganisms and parasites die. For quick conservation, dry ice is used, which emits carbon dioxide in contact with oxygen, or carbon dioxide.
In bags
In some cases, it is advisable to store the seeds in bags. Usually this applies to elite varieties of cereal, which must be separated from the main mass, or at the first collection of a new variety. For the manufacture of bags using coarse cloth, polyester, as well as paper bags.

When storing wheat in bags, it should be stacked on wooden pallets. The maximum height of the stacks should be 10-12 m.
Important! When choosing paper bags, you should pay attention to packaging made from special craft paper. This material is particularly durable and environmentally friendly.
Chilled method
The cooled principle of grain storage by technology is similar to dry, but it is more cost-effective and has low wheat losses. The grain is subjected to low-temperature processing, after which the vital activity of pathogenic bacteria on the surface of the cereal stops. With a refrigerated storage method, the desired cereal temperature is achieved with the help of supply and exhaust ventilation.

Permissible moisture limits and shelf life of grain
During storage, the grain mass, as experts say, “breathes”. This is an absolutely normal process associated with the vital functions of culture. Chemical processes in the seeds provoke the release of carbon dioxide and water. The difference in temperature in the granary and outside it, the level of moisture in the grain, as well as the specific features of cereal lots directly affect the harvest respiration.
Important! The increase in the intensity of “respiration” of cereals is directly affected by the presence of unripe seeds in the batch. Harvest with such impurities can deteriorate even with a sufficiently low level of humidity.
When choosing a granary, it is important to know how long the crop can be stored without loss of quality. With grain moisture not exceeding 13%, the shelf life of wheat can be 24 months in all regions of the country except the south. There, this period is halved. The same applies to grain storage, the moisture content of which ranges from 13% to 14%. In the south, such a crop can be stored for no more than six months, while in other regions, wheat has been lying well for 12 months.
 The farmers have an important definition - critical humidity, in the event of which the increased moisture content in the seeds enhances the "respiration", which causes spoilage of wheat.
The farmers have an important definition - critical humidity, in the event of which the increased moisture content in the seeds enhances the "respiration", which causes spoilage of wheat.
Winter
Winter wheat should be stored in rooms with an air temperature of + 5 ... + 8 ° C with a maximum grain moisture of 14%. Before sprinkling the crop in the granary, thorough disinfection of the premises should be made. In addition, in order to avoid an increase in breathing intensity, you need to regularly monitor the level of humidity and the temperature of the grain mass.
Spring
Spring wheat is suitable for storage when its moisture level does not exceed 14%. At the same time, the air temperature in the room can reach + 15 ° C. Unlike fodder, spring wheat grain is characterized by high humidity, therefore, it needs high-quality drying and cleaning. When storing spring wheat, an effective method of maintaining grain quality is active ventilation, which allows the cereal to self-heat.
Fodder
Feed wheat, that is, grain intended for animal feed, contains a large number of defective seeds.

This culture has a high starch content, at the same time with a low percentage of protein, as well as a minimal amount of fiber. The forage is rather well stored, however, the moisture content of such grain is lower - it should be no higher than 12%. The optimum storage temperature for the crop is + 8 ... + 10 ° С.
Important! Compared to other types of wheat, fodder is distinguished by good keeping quality due to the high content of carbohydrates that do not allow seeds to accumulate moisture.
The difference in weight of dry and raw wheat
Few people think about the difference in weight between dry and raw grain. When asked what is harder: a bag of freshly harvested cereal seeds or dry, most people will unequivocally answer: “Freshly harvested”. However, this is not the case. During storage, dry grain loses moisture. Due to this, its density increases, and with increasing density, the mass of cereal also increases.

Pest Control Methods
Even if it is possible to maintain the desired moisture level in the grain and not increase the intensity of its “breathing”, there is always the risk of damage to the crop by pests.
The most common parasites are:
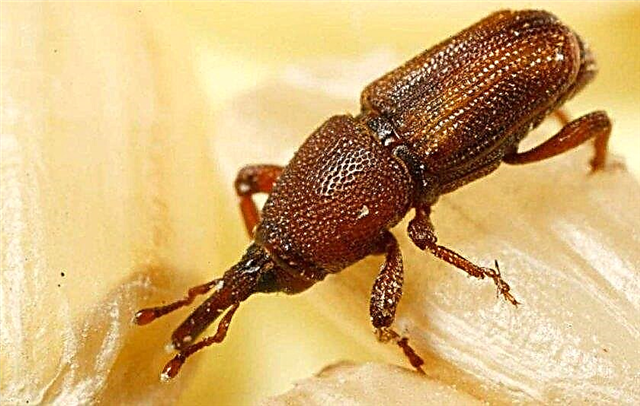
- Barn Weevilsthat lay larvae in recesses made in grains. The presence of an insect can be recognized by the characteristic cork on the seed.

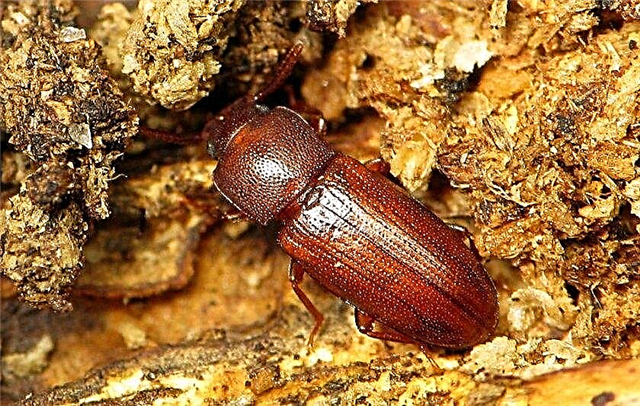
- Small Khrushchaks. These pests eat germ in the grain.

- Cereal and Barn Mothwhose caterpillars feed on wheat, gluing grains into lumps using a web. A characteristic sign of the development of insects in the crop is the pale color of the cereal, as well as the presence of empty grains with a side hole.

- Ticks. This insect, up to 1 mm in size, is not so easy to distinguish with the naked eye. Parasites feed on seed germs, and the female is able to lay up to 200 eggs per cycle.
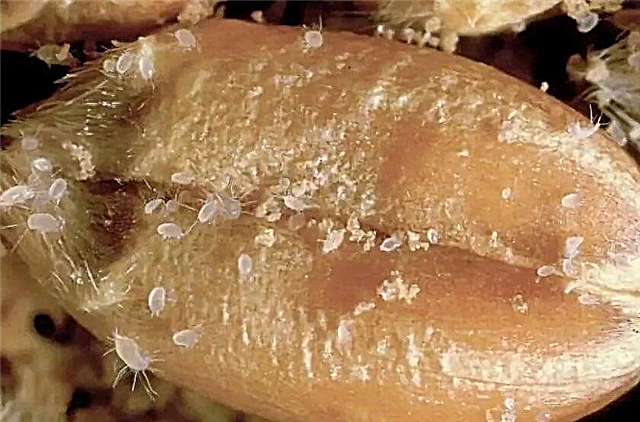
Prevention in the fight against parasites must begin even at the stage of preparing the field for sowing. To do this, the soil is treated with chemicals that impede the reproduction of pathogens. If the crop is damaged in the granary, it should be treated with special preparations.
It’s no secret that farmers and rodents who love cereals bring a lot of headaches. When uninvited guests appear, you need to set traps or decompose poison for rodents.
Did you know? Cereal insects stop reproduction and vigorous activity at air temperature below + 10 ° С.
By cultivating wheat, it is not enough to properly grow cereals and get a rich harvest. In order to preserve wheat, sometimes it takes no less effort than for its cultivation. Therefore, depending on the size of their crops and material capabilities, each farmer must choose the best way to store cereals so that losses are not critical.