Lack of nutrition of tomatoes worsens their normal development and reduces productivity. To get the most out of the culture, it should ensure a sufficient supply of the necessary substances. Let's get acquainted with the signs of a lack of various minerals in tomatoes, as well as when and how to feed them.
Signs of plant nutrient deficiency
Consider the symptoms of deficiency in tomatoes of the elements they need:
- Nitrogen. Old foliage near tomato bushes turns yellow (starting from the edges) and falls off. The plant withers and grows smaller, the stem becomes thin. The veins on the underside of the leaf blades acquire reddish and bluish tones.
- Phosphorus. With a deficiency of this mineral, the green mass becomes darker, then acquires a burgundy-violet hue. The leaves are wrapped, and the stalk becomes brittle.
- Potassium. Young leaves are wrapped down, becoming wrinkled. A burn appears along the edges of the leaves. The growth of the bushes becomes slow, the flowering becomes weak, but stepsons are actively developing. The fruits ripen with spots, the stalk has a yellow spot, and the pulp has hard veins.
- Calcium. Growth is slowed down, apical shoots may die out or apical rot will appear. Yellowish spots appear at the ends of the young leaves, while the old ones show a dark green color.
- Magnesium. Leaves bend up and dry along the edges, begin to turn yellow.

- Molybdenum. Yellow specks appear, the edges curl inward and dry out. The color of the leaves brightens, but the veins remain green.
- Zinc. New foliage is formed very small and is sometimes covered with yellow dots. Brown spots appear on the old foliage, exciting veins. The edges of the leaves are wrapped up. Over time, the leaves dry.
- Sulfur. Yellowing of the plant starting with young leaves. The stems become thin and brittle.
- Boron. Missing ovary. The top of the bush brightens and curls down. Stepsons are actively formed, and the upper point of growth perishes. Large veins of leaf blades noticeably darken, and the leaves themselves become brittle.
- Iron. Slowing growth and yellowing of leaves from the stem are observed. The top of the plant turns yellow. Veins at the ends remain green.
- Copper. Foliage fades and wraps with a straw. The shoots are weakened, and the flowers fall.
- Manganese. Foliage from the base begins to heterogeneously turn yellow, the plant looks mottled.
- Chlorine. New leaves poorly develop and brighten between the veins, fade.
Did you know? If there is a shortage of copper next to tomato bushes, it is recommended to stick a piece of copper wire, and with a lack of calcium — introduce crushed eggshells into the soil.
What time to feed?
Of course, if the plant shows a lack of a certain element, then it is necessary to make the appropriate fertilizing. With a lack of nitrogen, urea should be used, with a lack of phosphorus - superphosphate, and with a lack of potassium - potassium nitrate.
Tomatoes begin to feed already while receiving seedlings. After planting it in the ground, usually 3 top dressings are done - after planting, when the bushes bloom and during fruiting. In general, the number of procedures depends on the state of the soil - on poor soils you can feed every two weeks.
It is best to feed the beds in the morning or in the evening. When fertilizing open beds, weather conditions are taken into account.
Types of Feeding
For tomatoes, two types of top dressing are used - root and foliar. It is most effective to alternate them.
Root
This type of fertilizing is absorbed by the root system of culture. Usually, fertilizer is placed under the roots during planting, or nutrient solutions are poured under the bushes. This method is considered the most important for nutrition. Both natural and special chemical compounds can act as fertilizers.
Important! When watering fertilizing tomato bushes, try not to get on the green mass of the plant, as this can cause a burn.
Foliar
With this feeding, the assimilation of elements goes through the green mass of the plant. She begins to feed and act immediately, so foliar treatments are often used as an ambulance for a plant or when the roots cannot or do not have time to absorb everything that is needed from the soil. Typically, the concentration of substances used in such solutions is not more than 1%. Exceeding the norm can cause burns to the leaves. Some of these top dressings not only nourish tomatoes, but also protect them from diseases.
Among the foliar treatments of tomatoes, the most popular products with the following elements:
- boric acid - to preserve the ovary;
- iodine and serum - to increase resistance to fungal diseases;
- onion peel - nourishes and improves immunity;
- "Trichopolum" - against late blight;
- weak potassium permanganate solution:
- ammonia.
In some cases, foliar top dressing is a necessity:
- in acidic or heavy, dense soils, since under such conditions the root system does not absorb food from the earth;
- with damage to the roots;
- You have found strong signs of a lack of a specific item;
- at the beginning of budding and flowering;
- if the earth is too wet;
- if signs of disease are found.
Important! When performing foliar top dressing, it is necessary to select calm weather and check the weather forecast so that there is no precipitation.
Fertilizers for tomato seedlings
Seedlings grow in limited conditions and require the addition of fertilizing:
- the first is carried out when 2-3 leaves appear or 10-14 days after the dive;
- the second is done 14 days after the first;
- the third and subsequent nutritional procedures are done every 10 days and stopped a week before disembarkation.

You can make yourself a natural feeding mixture of ash and organic matter (manure, bird droppings). In a 10-liter bucket dissolve a handful of ash and 3 tables. tablespoons of organic fertilizer.
It is also good to apply onion peel. To do this, onion husk from three onions is poured with 0.5 l of boiling water and insisted for several hours, and then the plants are watered. For spraying, the husk is insisted on cold water.
How to feed tomatoes
There are various fertilizers used to power tomatoes.
Did you know? Urea (urea) was first detected in urine, for which it got its name. The production of urea by the chemist Wöhler in 1828 was the first synthesis of organic matter from inorganics.
Simple mineral fertilizers
Most of all, plants need three minerals for nutrition - nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus.
Simple mineral fertilizers are divided according to the content of these substances into three types:
- Nitrogen. They are necessary for the formation of green mass and are very important for seedlings and subsequent growth before flowering. The most popular are urea, ammonium sulfate, ammonium nitrate. It is enough to part 1 table. spoon in a 10-liter capacity.
- Phosphoric. Needed for root formation. Usually represented by superphosphates. They dissolve poorly. Simple superphosphate is poured with boiling water (1 table. Spoon per 1 liter of boiling water) and insisted for a day, then diluted in a 10-liter container and used.
- Potash. Promote the development of roots and good immunity of tomatoes, improve their taste. Potassium is required for the plant throughout life, especially during the cultivation of seedlings. Potassium fertilizers include potassium sulfate (40 g / 10 l), potassium nitrate (25 g / 15 l), kalimagnesia, which is added to the soil during digging (10 g / m²) or is made using it by spraying (20 g / 10 l )

Organic fertilizer
Natural organic is always popular with gardeners. Such fertilizers contain a rich composition of elements and well raise the level of yield.
Most often, the following tools are used:- Manure. Contains all the main minerals and many auxiliary elements. For liquid top dressing of tomatoes, a rotted product is used. To prepare a mullein, a bucket of manure is mixed with 4 buckets of water and left for several days until it is fermented. Before use, the resulting solution is diluted with water 1: 4. The overripe mullein is bred with water 1:10 and insisted only for a day. Such a solution can be used even for foliar top dressing. On sale now there is a ready-made mullein.
- Bird droppings. It requires low concentrations, as it can cause burns to the plant. It is diluted 1: 1 with water and allowed to ferment for several days, after covering it. The resulting mixture can be stored for a long time. The finished solution is diluted 1:10 and poured into the wells; it is advised to apply at least two times.
- Compost. It can be done on its own in compost pits from organic debris and food debris. It is usually added to the holes when planting tomatoes.
- "Green manure". Shredded weeds are poured with water and kept in the sun. Ready herbal infusion is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:10. Nettle is considered the best plant for such a remedy.
- Humates. Salts of humic acids improve any soil, increase the resistance of tomatoes to adverse factors. They are usually obtained from peat or coal and are often used with mineral complexes. For top dressing, dilute 100 ml of concentrate in a 10-liter container.

Folk remedies
Among gardeners, homemade products are popular, which in effectiveness often exceed the purchased ones. They often have a multicomponent composition, and in them organics are used in conjunction with inorganic compounds.
Consider the popular folk remedies used to fertilize tomatoes:
- Ash solution. In a 10-liter bucket, dilute 1 cup of ash powder and leave for several hours. Such top dressing contains many useful elements, it can be used every 14 days.
- With mullein. In a 10-liter bucket, 1 liter of mullein and 15 g of nitrophoska are mixed with water.
- With chicken droppings. In 10 l of water, stir 0.5 l of infusion of chicken litter, 2 tables. tablespoons of superphosphate and 1 table. a spoonful of potassium sulfate. Superphosphate in some recipes is replaced with 7 g of boric acid.
- Simple yeast. 2 kg of pressed yeast are dissolved in 10 l of water and left for a day. Then 0.5 l of yeast infusion is mixed with a bucket of water.
- Integrated. In a large capacity (200 l), a third of the volume is filled with weed grass. Add a bucket of mullein, 2 l of ash, 2 kg of yeast, 3 l of serum and insist all 14 days. Then, in a 10-liter bucket, dissolve a liter of the obtained product and use it.
Did you know? Tomatoes began to grow in Russia as an ornamental plant, since the culture did not have time to ripen. Only at the end of the 18th century did the Russian botanist and writer Bolotov make the tomato culture accessible for consumption using the seedling method and ripening.
The most famous foliar top dressing:
- From iodine and whey. To make it, you first need to mix 8 liters of water and 2 liters of serum, then add 3 cups of granulated sugar and 20 drops of iodine. The tool perfectly enhances the immunity of the bushes and nourishes them.
- To improve the taste. In a 10-liter bucket of water, dissolve 10 ml of boric acid from the pharmacy and 3 drops of iodine.
- To increase the number of ovaries. In 10 l of water add 2 l of ash and 10 ml of boric acid.
- Against late blight. In a 10-liter bucket of water, dissolve 10 tablets of Trichopolum and 1 bottle of green stuff.
Complex fertilizers
There are mineral complexes containing several types of elements.
The following complex fertilizers for tomatoes are most popular:
- Diammofoska. Consists of three main elements, it is well dissolved. For top dressing, 2 teaspoons are bred in a 10-liter bucket of water.
- Ammofoska. It consists mainly of phosphorus (50%), but also includes nitrogen (10%). The product is water-soluble, recommended for use at the beginning of the season (50 g / 10 l).
- Nitroammofoska. The ratio of nitrogen / potassium / phosphorus is as follows - 1: 1: 1. It is well dissolved and divorced for top dressing of 50 g / 10 l.

Features of fertilizer application
For all the time, tomatoes need to be fed at least three times - after planting on the beds, during flowering and during the formation of berries.
After landing in the ground
The first top dressing is carried out 2 weeks after the planting of seedlings in the soil. This will strengthen young tomatoes and allow them to adapt quickly to a new place. For further growth and development, it is necessary to select a complex of fertilizers that will help increase the green part of the plant so that the bush can withstand the weight of the fruits in the future.
Gardeners recommend the following types of top dressing:
- 0.5 kg of fresh manure, 30 g of nitrofoska stir in a 10 liter bucket of water;
- Dilute 0.5 kg of rotten bird droppings, 30 g of superphosphate and 15 g of potassium sulfate in 10 l of liquid;
- 60 g of nitrophoska or 60 g of calcium nitrate per 20 l bucket of liquid.
Did you know? The word "tomato" came to us from Italy and means "golden apple".
To fertilize larger areas with plantings, the following fertilizing solutions are recommended:
- 10 l of mullein, ½ bucket of ash, 2 kg of yeast, 3 l of whey, 4 armfuls of nettle are dissolved in 200 l of water and allowed to infuse for 8–9 days;
- 5 kg of chopped nettle, 5 l of mullein, 0.5 kg of ash mix in 50 l of liquid and let it brew for 14 days. Then add the resulting mixture to 100 liters.
Under 1 bush is 0.5 l of the above mixtures.
During flowering
Blooming tomatoes need phosphorus and potassium, but the need for nitrogen is reduced to a minimum. This is important for the formation of more color and ovary. Top dressing should be done during the appearance of buds on the second brush of the bush.
Recommended feeding pattern during flowering:
- In 10 l of hot water, 2 l of ash, 10 g of boric acid are diluted and allowed to infuse for 24 hours. Under each bush is 1 liter.
- Dilute in 10 l of liquid 30 g of superphosphate, 15 g of potassium sulfate. 0.5 L is poured into each well.
- In 10 l of liquid, mix 400 g of rotten chicken droppings, 10 g of potassium sulfate. Under the bush, pour 1 liter of the mixture.
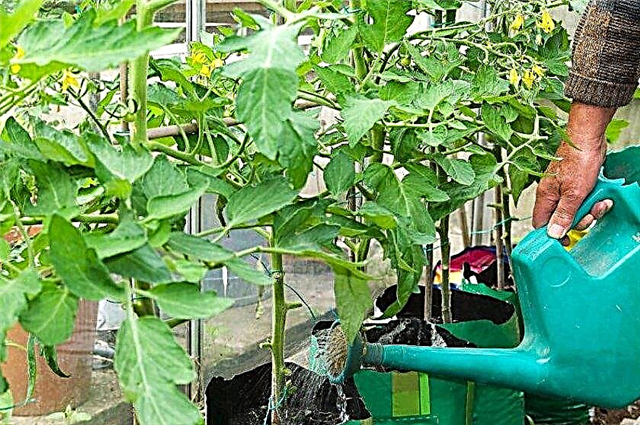

Foliar spraying also gives excellent results:
- Dilute 2.5 l of cow's milk and 14 drops of iodine in 10 l of water. Such treatment is also an excellent prevention of late blight.
- Pour 1 liter of boiling water 60 g of superphosphate and let it brew for at least 12 hours. Then add up to 10 l and spray.
- Throw 5 g of boric acid into a 10 liter bucket of liquid. Spraying with such a solution must be carried out when shedding color from the heat. This procedure is also the prevention of apical decay.
During fruiting
In the period of fruit setting and growth, fertilizers containing potassium are used. In this case, nitrogen-containing components should be completely eliminated, since they lead to the growth of green mass, which will pull the nutrients onto itself, which will significantly slow down the formation of tomato fruits and reduce their size.
Gardeners with extensive experience recommend such dressings:
- 15 ml of water take 15 ml of potassium humate and 20 g of nitrophosphate. Everything is thoroughly mixed and poured under 1 plant of 1 liter.
- 100 g of yeast and 120 g of granulated sugar are stirred in 2.5 l of warm water. The mixture is left in a warm place for 7 days.For 10 liters a bucket goes 0.5 liters of such a mixture, 200 g of wood ash is added there.
- 60 g of superphosphate, 30 ml of sodium humate are diluted in 10 l of liquid. Pour 1 liter of agent into each well.
- 25 g of magnesium sulfate, 10 g of potassium nitrate are dissolved in 10 l of water. Under 1 bush is 0.5–1 liters.
What is the danger of lack of trace elements?
Deficiency of substances necessary for the nutrition of tomatoes, badly affects the growth and development of plants, reduces yield. When such a phenomenon occurs, the plant itself will signal this with certain signs. In this case, you need to carry out extra feeding with the content of the missing elements.
With a lack of trace elements, plant immunity usually falls, and tomatoes become susceptible to late blight and other diseases.
An overabundance of elements also negatively affects the culture. For example, with an excess of nitrogen, yield decreases, ripening is delayed, the plant is poorly resistant to disease. Accordingly, it is always necessary to observe the recommended concentration of fertilizers, and when using organics, reduce the dose of mineral fertilizing.

Additional Tomato Care Tips
Specialists also give the following recommendations for the care of tomatoes:
- When grown in a greenhouse in late summer, top dressing should be applied until the end of August every 10 days to accelerate the formation of fruits. The recommended composition is 15 g of potassium monophosphate or 10 g of kalimagnesia per 10 l of liquid. So that the nutrients go to the formation of fruits, you should also pinch the top of the bushes.
- When applying fertilizers, the rule should be observed - it is better to undernourish than to overfeed.
- Starting from the flowering period and until the fruit is harvested, pesticides cannot be used.
- Root top dressing should be combined with watering of plantings, and foliar - with spraying from insect pests.
Fertilizing tomatoes can be done on the basis of mineral fertilizers, organics, folk remedies. The main thing is to give the plant the necessary nutrition on time, but not to overfeed it at the same time.