In order to get 100 g of honey, a bee in search of raw materials must fly 46 thousand km - this distance corresponds to the length of the equator. Due to the laboriousness of the honey collection process, many beekeepers specially sow long flowering perennials with copious amounts of nectar and pollen near the hives, thereby launching a continuous flower conveyor from early spring to late autumn. Find out which honeybearing plants beekeepers recommend for the temperate climatic zone, when to sow them and how to alternate - you will learn further from the article.
Features of honey plants
If initially the feed base of bees consisted of flowering trees, shrubs and meadow forbs, then modern beekeepers have expanded bribes with specially sown crops, which at times increase the productivity of honey collection.
Did you know? An average bee family can collect up to 10 kg of honey per day. To do this, she will need to visit about 80 million flowers.
Botanists isolate melliferous trees, bushes and grasses into a separate group of angiosperms, the flowers of which are characterized by unique glands that produce sugary liquid. These are nectaries, which may consist of flattened dots, strongly elevated tubercles or indented grooves at the base of the buds.
Abundant bribes are possible from wild meadow and forest grasses, as well as from specially grown, agricultural, fruit, park, and ornamental crops. Among them, the most promising beekeepers consider: clover, sunflower, buckwheat, acacia, maple, linden, clover, fatseliya.
The peculiarity of these plants lies in the intensive production of nectar during the flowering period, based on evolutionary processes aimed at cross-pollination of flowers with the help of insects.
The period of budding and cotyledon formation, as well as the amount of sugar released, depends on the biological characteristics of each type of vegetation, climatic and geographical factors. An unstable indicator of the produced nectar and pollen is affected by the time of day. In some perennials, more of it appears in the morning (for example, oregano, vetch), in others - in the afternoon (phacelia, honeycomb), and in others - in the evening (Lungwort).
In sunny weather, bees collect nectar, processing it for honey and bee bread. If the bribe was obtained from cherries, poplars, birch or other plants that produce resinous substances, then the final product of insects will be propolis and ouza.
It is characteristic that most honey plants have medicinal properties, but the amount of nectar secreted by one flower is different. For example, in linden this indicator is 0.14–7.55 mg, in clover - 0.19 mg, and in tropical orchids - 30 g. Moreover, not all plants are characterized by dustiness.
Did you know? Every day, in search of food, bees explore an area of about 12 hectares.
Honey plant classification
Bees can get a good bribe to the same extent from grasses as well as from bushes or trees.
Depending on the time of the appearance of peduncles, all plants with abundant formation of nectar are classified into several types:
- early spring (willow);
- spring (most fruit crops);
- summer (sunflower);
- autumn (peppermint).
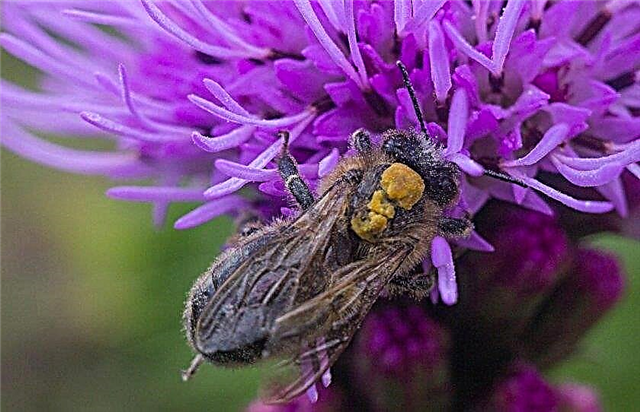

Based on the characteristics of flowering plants, among them can be distinguished:
- nectaronoses - These are very rare plants that have extra-flowering nectaries (vetch);
- dust carriers - characterized by a nondescript, but plentiful flowering without bright petals (birch, elm, grapes, hazel);
- nectar dust (acacia, buckwheat).
Trees and bushes
The names of honey plants common in the temperate zone can be found in the tables below.
Fruit trees:
| Name of culture | When blooms | Qualitative characteristics of honey |
| Apple tree | Throughout May (depending on variety) |
|
| Cherry | The last April decade | specific light color |
| Pear | The last decade of April | specific light color |
| Cherries | Starts in the second decade of April | transparency |
| Plum | Mid spring | whitish tint |
| Cherry plum | First half of april | — |
| Apricot | Last 2 weeks of April | — |
| Peach | April | — |
| Quince | Beginning of april | — |

Other types of trees:
| Name of culture | When blooms | Qualitative characteristics of honey |
| Linden | The last decade of June | light shade of amber color |
| Maple | First half of april | — |
| Willow | First decade of April |
|
| White Acacia | The end of spring - the beginning of summer |
|
| Horse Chestnut | The end of spring - the beginning of summer |
|
| Sophora Japanese | Second half of summer |
|

Shrubs:
| Name of culture | When blooms | Qualitative characteristics of honey |
| Currant (black and red) | Early spring (before flowering trees) | — |
| Raspberry | The beginning of June |
|
| Blackberry | From mid-May to mid-June |
|
| Barberry | Last May Decade |
|
| Blueberries | Early May - Mid June |
|
| Viburnum | After the apple trees (flowering lasts about 2 weeks) | — |
| Sea buckthorn | From the second half of April to the end of May | — |
| Rowan | Mid may |
|
| Buckthorn | From late spring to early fall |
|
| Heather | In August and September |
|

Grass and flowers
To increase the productivity of honey collection, experienced beekeepers sow one- and perennial nectar-bearing plants in the apiary. It can be field or feed agricultural, essential oil, medicinal herbs or decorative flowers. The main thing is that they are stunted.
Important! Honey that has been crystallized is strictly forbidden to melt at a temperature above + 50 ° C. This is due to toxic substances formed in the product, which are very harmful to human health.
Outside the place where the hives are located, you can plan crops of tall crops. When cultivating them, it is important to consider not only the flowering period, but also adaptability to the climatic conditions of a particular region. After all, not all honey carriers can adapt to the sharp heat-moisture differences characteristic of the middle band. Dry summers, harsh winters, early or late spring, variable atmospheric circulation and frequent cyclones are well tolerated by the plants below.

Spices:
| Name of culture | When blooms | Qualitative characteristics of honey | |||
| Sage | Second half of summer |
| |||
| Melissa | Second half of summer |
| |||
| Borago | Second half of summer |
| |||
| Mustard | white | June August |
| ||
| gray | First half of summer |
| |||
| Coriander | The last decade of June - early July |
| |||
| Snakehead | It blooms for a month from the second half of July to August |
| |||
| Lavender | June August |
| |||
| Mint | All summer long |
| |||
| Caraway | The end of spring - the beginning of summer |
| |||
| Anise | First half of summer |
| |||

Feed grasses:
| Name of culture | When blooms | Qualitative characteristics of honey | |||
| Phacelia | Early summer |
| |||
| Bruise | First half of summer |
| |||
| Clover | white and pink | — |
| ||
| red | June August |
| |||
| Alfalfa | sowing | — |
| ||
| crescent | All summer | ||||
| Sainfoin | The last decade of May - early June |
| |||
| Donnik | annual | A large number of |
| ||
| biennial | Blooms in the second year in mid-June for 40–45 days |
| |||
| Vika | The second decade of May - mid-June | — | |||

Other types of herbs:
| Name of culture | When blooms | Qualitative characteristics of honey | |||
| Mignonette | All summer |
| |||
| Buckwheat | The second decade of June |
| |||
| Sunflower | Beginning of July - September (depending on the timing of sowing) |
| |||
| Rape | winter | Plentiful, lemon |
| ||
| spring | June July | ||||
| Cotton | Summer is the beginning of autumn |
| |||
| Motherwort (officinalis) | The second decade of July - the beginning of autumn |
| |||
| Marshmallow | It blooms in the second year from the second half of July to mid-August |
| |||
| Angelica | It blooms in the second year from June to August |
| |||

The listed herbs are ideal for large and small fields. They develop well in the steppe and forest-steppe zones, mountain and piedmont massifs of the northern, central, southwestern zones of the Russian Federation and in the suburbs.
According to experts, the most productive in terms of beekeeping region of the Russian Federation is Bashkiria. This fact is due to the uniqueness of honey plants, which local botanists have more than 350 names. The local nature is so rich and diverse that sometimes you can’t even think that 2 different varieties were obtained in the same locality. That is why experts distinguish meadow, mountain Bashkir honey, and also classify it according to honey plants (melilot, acacia, linden, etc.).
In the harsh conditions of Siberia, weeds are the main source of nectar and pollen.Did you know? The most expensive honey is produced in Israel. Local beekeepers sell kilograms of bee products for $ 17–20.
In particular, we are talking about:
- hemlock speckled - grows everywhere, is characterized by high nectar and dust content, is well visited by bees;
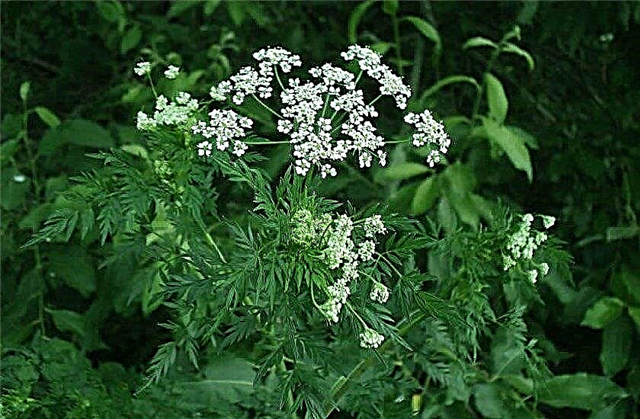

- artifact swamp - prefers marshy meadows, forest glades and shrubbery; its honey productivity corresponds to 300 kg / ha;

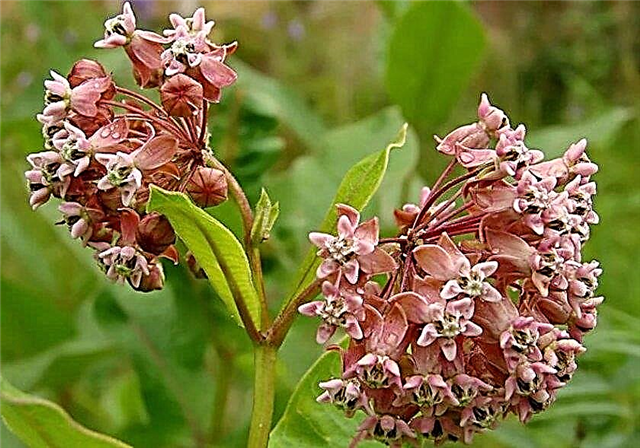
- Syrian - even a small amount of this grass in agricultural crops leads to significant losses in yield. Bees visit this plant well and collect up to 250 kg of nectar from it (per hectare of whole area);

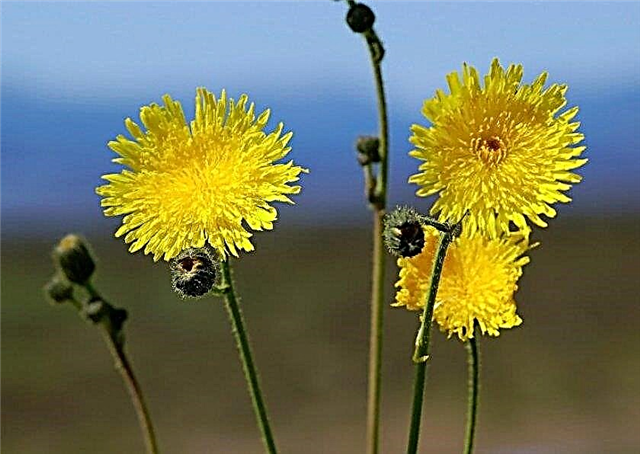
- field sow thistle - found everywhere, gives a lot of pollen and nectar, honey collection is 380 kg / ha;

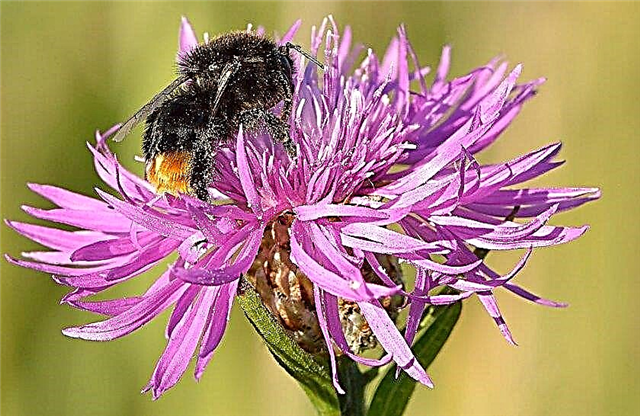
- cornflower meadow - represents a group of nectar-dust-bearing plants, is well visited by bees, its honey productivity in terms of continuous massifs is more than 110 kg / ha;

- milkweed spicy - this weed is a good honey plant and at the same time an aggressor, because it displaces all plants growing near it. Its honey productivity is 250 kg / ha.
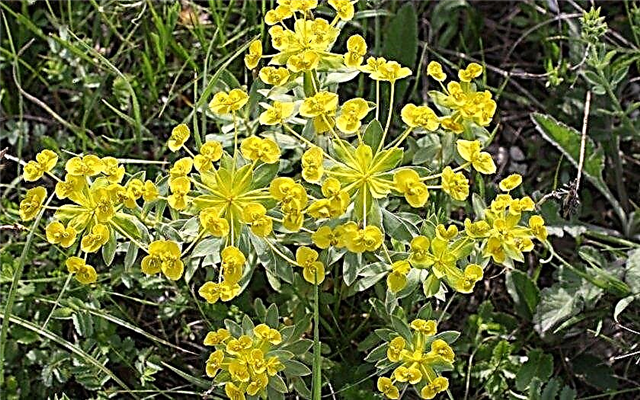

Types of the best honey plants
In order to properly draw up a flowering calendar of nectar-pollen beet plants for a particular area, you should familiarize yourself with the best honey plants of the country.
Melilot white and yellow
Both types of clover are two-year-old tall plants with ternate foliage and densely branched stems, at the end of which flower brushes form. In the white variety, their length is much shorter compared to yellow.
They bloom annually throughout the summer, at times increasing the number of buds in the second growing season. Then the seeds ripen. From each hectare of continuous sowing, you can collect up to 12 centners of planting material (it is better to do this in September). It is sown for fodder and melliferous purposes.Important! Honey can cause allergic reactions, therefore it is categorically contraindicated for allergy sufferers.

Sweet clover is widely distributed in the Central Russian strip, less common in the West Siberian regions. This wild weed can be seen in meadows, roadsides, steep coasts, rocky slopes, and even near the dwellings of the local population.
The plant is nectariferous and does not emit pollen at all. Bees can collect about 0.5 milligrams of raw material from each flower, but due to the fact that the stems are densely covered with buds (on average, their number reaches 10 thousand), the honey properties of the grass are very high.
According to experts, the nectar productivity of sweet clover is different and depends on the geographic and climatic conditions of a particular region. For example, in the Voronezh region it reaches 170 kg / ha, and in the Novosibirsk - 270 kg / ha.
The highest attendance of the honey bee by insects was recorded at a temperature of + 25 ° C and air humidity at 60% (mainly from 13 to 17 hours).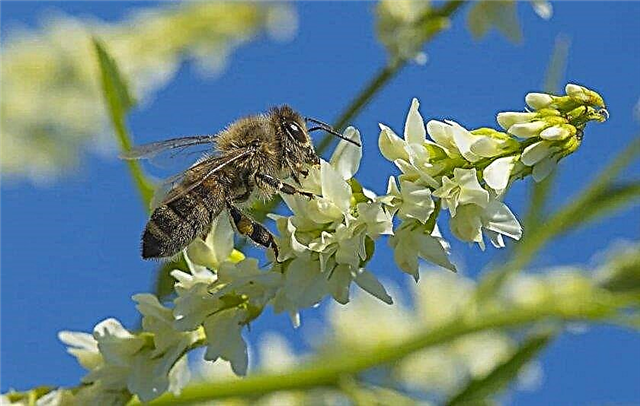 The white and yellow types of sweet clover tolerate drought, but in conditions of excessive heat, when the thermometer rises above + 30 ° C, the plant grows poorly and is characterized by worse melliferous qualities.
The white and yellow types of sweet clover tolerate drought, but in conditions of excessive heat, when the thermometer rises above + 30 ° C, the plant grows poorly and is characterized by worse melliferous qualities.
Did you know? In ancient Rome, honey was regarded as a currency. A delicacy could pay for the goods and pay fines.
Hyssop
A perennial plant is characterized by thick-growing upright stems up to 1 m high - they develop in the form of a bush with a lignified root part. The elongated foliage is opposite, it has a rich dark green color, smooth edges and a pointed tip.
Preferred for hyssop are loamy sunny areas. This is an unpretentious grass that tolerates drought and harsh winters, in favorable conditions it can develop over 10 years. But excessive rainfall can destroy the plant.
Hyssop bloom begins in the second half of summer and lasts until the beginning of autumn.Buds with a lip-colored structure come in blue, purple, purple, scarlet, white and blue petals. They form spike-like inflorescences that open gradually.
For beekeeping, hyssop is valuable as a source of nectar and pollen, which insects collect mainly in the morning. From each hectare of sown area, bribes in the range of 120–150 kg are possible. It is characteristic that every year the plant’s honey production increases.
Did you know? The word "honey" of Jewish origin and literally means "one that is endowed with enchantment."
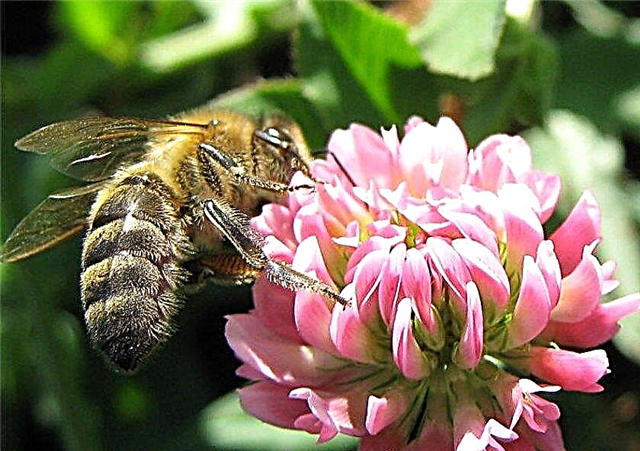
Clover
Culture represents the Bean family, it is annual and perennial. Recognizable by its bushy shape, dissected by three- or five-lobed foliage, moth flowers of pink, white or red, purple.
This grass is one of the most important feeds in agriculture, as well as the leading honey plant. It releases pollen and nectar in large quantities.
Mass flowering of clover begins in June and lasts for one month. Intensive honey collection is promoted by a temperature in the range of + 24 ... + 28 ° С, as well as humidity at the level of 60%. Under such conditions, bees can collect about 140-200 kg of raw material from each hectare of clover field.
A feature of the culture is that each bush forms from 50 to 90 bright beautiful flowers that attract from the vicinity of pollinating insects.

Lofant
This plant in folk medicine is known for its many medicinal properties, but in the Russian Federation it is not registered as a medicinal one.
Perennial grass develops to a height of 2 m and is distinguished by long brownish-bluish leaves, reaching a length of 10 cm, thick branches, bushy form, long flowering.
The first purple and white buds on the stems open with the advent of summer and wilt after about 3 months. In their place, small grains of dark color ripen.Nectar productivity of the plant is very high, due to its ability to secrete a sugary liquid substance throughout the day, regardless of weather conditions. The bee bribe from the Lofant field is 550 kg / ha.
Such honey is characterized by high-grade signs and possesses general strengthening, immunostimulating qualities. Grass is specially sown on fertile light soils.
Spherical muzzle
It is a perennial bush up to 2 m high with single upright hairy stems, long cirrus foliage, spherical inflorescences, consisting of tubular buds.
The muzzle blooms in early summer with white or blue flowers, and its fruiting begins closer to mid-summer. Then, from the peduncles ripe cup-shaped achenes.
Grass is common in the Russian Federation, Ukraine, Central Asia and the Caucasus. More often it can be seen in meadow and steppe zones. In many countries, it is cultivated as a medicinal raw material and an outstanding honey plant.
The spherical-headed muzzle intensively secretes nectar, often filling them with all inflorescences, and also gives whitish pollen. Active attendance of the plant by bees is observed in sunny warm weather. Under such conditions, a bribe of 1050 kg / ha is possible. The honey obtained is characterized by medicinal properties, as well as a weak aroma, excellent taste, transparency and colorlessness.Important! When buying honey, consider that more often fake light varieties.

Phacelia
We are talking about annuals with upright stems up to one meter high, with thick side branches, cirrus leaves and lilac-blue miniature bell-shaped flowers. Inflorescences consist of about 5-10 buds.
In the care, the grass is unpretentious, adapts well to any substrates, is not sensitive to diseases and pests.
Phacelia flowering begins a month and a half after sowing and lasts about 45-50 days.For enhanced honey collection, experienced beekeepers sow the plant in several stages, which in one season allows insects to provide up to 4 flower-bearing periods.
Inflorescences of this culture are characterized by high honey production: each flower during the day releases up to 5 mg of nectar. As a result, bees from a hectare of the Phacelium field can collect about 650 kg of raw materials.
Since the flowering of phacelia lasts all daylight, experts consider it a leader among grassy honey plants.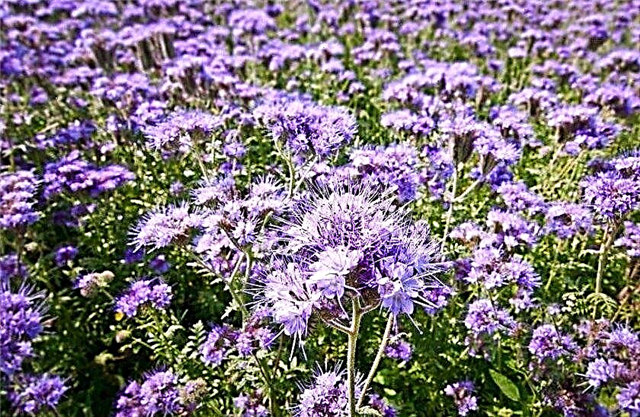
Linden
This is a luxurious slowly growing tree up to 30 m high with dark bark, dense branches, heart-shaped leaves and fragrant inflorescences.
Culture intensively develops crown up to 80 years, and the duration of its development is no more than 120 years. Flowering begins in the second half of June and lasts for 2 weeks (in the northern regions, linden flowers appear in the last decade of July).
Botanists distinguish different types of lindens, which differ in the size of the foliage and the characteristics of peduncles. On the territory of the Russian Federation, small- and large-leaved, Amur, and Manchurian varieties are more common.
A feature of the plant is increased demands on soils and growing conditions. These trees develop best in forest areas on podzolic, loamy, sandy or sandy loamy soil. They also do not tolerate drought and excessive moisture.According to experts, linden belongs to the leaders of nectariferous crops, but does not produce pollen. From each hectare of linden forest, bees can collect about 1200 kg of raw materials before sunset. This means that one tree provides a bribe of 10 kg. With an abundance of forest stands, the bee family collects up to 60 kg of honey.

What is the best way to sow honey plants?
Those who have been breeding bees for more than one year know which of these melliferous plants listed above is characterized by the best efficiency for a particular region. In order not to be mistaken for beginners, you need to create a special calendar, planning it so that the crops bloom unceasingly.
In order to provide the apiary with a stable supply of nectar, large areas are required. Accordingly, small landowners plant apiary with nectar-bearing trees and bushes, which helps maintain a working mood in the hives throughout the season.
It is important to create a melliferous environment around the hives from the main sources of nectar: clover, linden, cyanosis, phacelia. It is advisable that these crops are within a radius of no more than 1.5 km.
Experienced owners advise sowing biennials under the cover of annual herbs: for example, sweet clover under alfalfa, a bruise under fatseliya.
Honey plants with later vegetation are recommended to be cultivated to collect seed material. And to extend the period of budding, you need to mow some of the grass crops until mid-June.
Between the hives, nectar-bearing weeds and ornamental crops are welcomed - Lungwort, motherwort, dandelion, sweet fruit, mint, lemon balm.

Is it worth it to sow special plants on your site or is it easier to take the hives to the melliferous fields and lawns, you decide. The main thing is that bee colonies should be provided with access to nectar and pollen throughout the season.