Cucumber is a common vegetable crop that everyone grows on his own plot of land. Despite the plant’s popularity, problems with growing it are quite common, especially if the crop grows in a greenhouse. Here the question of how to overcome the yellowing of the embryo is always acute. This will be discussed in this article.
Causes of Yellowing Cucumber Germ
For normal growth and development, the cucumber needs heat and moisture. If these parameters do not correspond to the norm or other rules of agricultural technology of culture are violated, the embryos of Zelentsy cannot develop normally.

Violation of optimal temperature and humidity
In the middle zone at the end of May, sudden frosts after a well-established heat are quite frequent. Because of this, the seedlings of cucumbers growing in a film greenhouse can turn yellow and even slow down in growth. Temperature jumps above + 30 ° С are also negatively reflected. Under the scorching rays of the sun and in conditions of low humidity, the plants quickly begin to turn yellow and shed their ovaries.
Did you know? Previously, in order to ensure normal pollination of cucumbers, hives with bees were carried out to the fields where they grew.
Lack or imbalance of nutrients
Usually, if there is not enough nitrogen in the soil, then the leaves of the cucumbers begin to turn yellow. The process starts from the ends of the leaf and gradually moves to the lashes of the plant. To change the color of the bush, a change in the shape of the fruits is also added (they become twisted). To provoke a lack of an element is capable of introducing a large amount of wood ash, potash fertilizers, superphosphates.
Wrong watering
Cucumbers are a moisture-loving culture, but they will not survive the excess moisture. This leads to the development of root rot and the gradual death of the bush. The lack of moisture, both in the soil and in the air, also has a negative effect. This is especially noticeable during the fruiting period. Zelentsy formed irregularly, small and bitterly. The culture is also sensitive to water temperature. When watering with cold water, the leaves and ovary begin to turn yellow.
Thickened landings
Often, wanting to use the area of the greenhouse as efficiently as possible, gardeners plant cucumber bushes close to each other. This leads to the fact that those nutrients that are contained in a small piece of land that falls on one bush are not enough for the growth and development of the fruit. Even at the stage of ovary, they begin to wither and fall.
In addition, a dense planting leads to the fact that due to the tight plexus of foliage, the plant receives less sunlight. As a result, the process of photosynthesis does not proceed normally. Because of this, the foliage begins to turn yellow, and the fruits lose moisture and shrink. Another thickened planting contributes to the more rapid development of various diseases that affect the condition of the ovary.
Overripe cucumbers
The presence of at least one overgrown fruit on the bush significantly inhibits the development of the remaining ovaries. Even if the overripe Zelentsy sags an extra two hours on the lashes, then it will already affect the growth of the rest.
Important! A negative effect on the process of fruit development and a large number of embryos on the bush. Normally, it is advisable to leave 20–25 greens.
Pests
Although the greenhouse is an isolated space from external conditions, pests can get into it. They can be brought in with soil, tools. Most cucumbers in the greenhouse bother:
- Gourd aphids. This small, almost imperceptible pest settles on the back of the leaf and drinks all the juices from the plant. As a result, the entire bush begins to wither, along with the ovary.

- Spider mite. Another tiny pest that prefers the back of the leaf. Wrapping a plant with small cobwebs, it disrupts the course of natural processes in the bush, due to which it gradually begins to die.
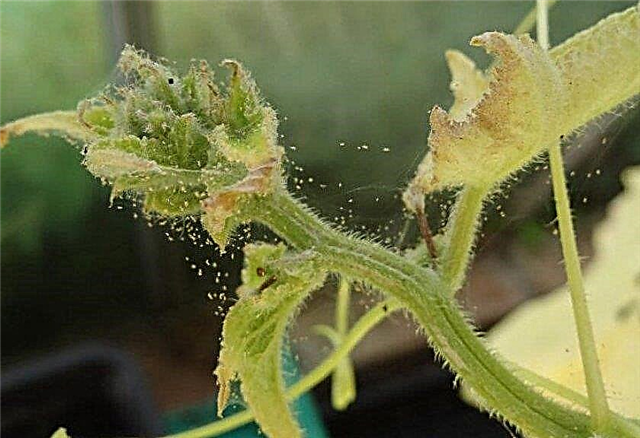

- Whitefly. It comes to the crop from weeds and first causes the decay of the foliage, and then the entire plant, including the fruits.

Pollination problems
It is difficult for insect pollinators to get into the greenhouse, because of this the pollination process may not occur. As a result, the ovary, which was on the female flowers, begins to fall. Therefore, greenhouses cultivate self-pollinated varieties or those in which the pollination process occurs artificially. But there are problems with them, if the plant blooms poorly or help in pollination was not provided in a timely manner.
Ways to combat diseases and pests
All of the above problems are easily solved, but you still have to make some efforts.
Proper lighting
Without light, not a single plant can grow. If there is lighting, but of insufficient intensity and short duration, then growth will be, but weak. Therefore, it is very important that cucumbers at all stages of development receive a sufficient amount of light. During the day, a total of plants should be lit at least 12 hours, while 6 hours they should be in complete darkness.
With a lack of natural light, it is necessary to apply illumination.
For these purposes, you can use:
- fluorescent lamps (emit a spectrum suitable for plants, durable, but able to illuminate a limited space);
- sodium (emit monochrome light of the orange-yellow spectrum, have high light output, are effective during the flowering period of the crop, but are unsuitable in the vegetative phase of growth of the bushes);
- metal halide (they have a wide spectrum of radiation and a wide power range, their light is the closest to the sun, but they do not last long and cost a lot);
- LED (easy to install, well illuminate the greenhouse, but cost a lot).
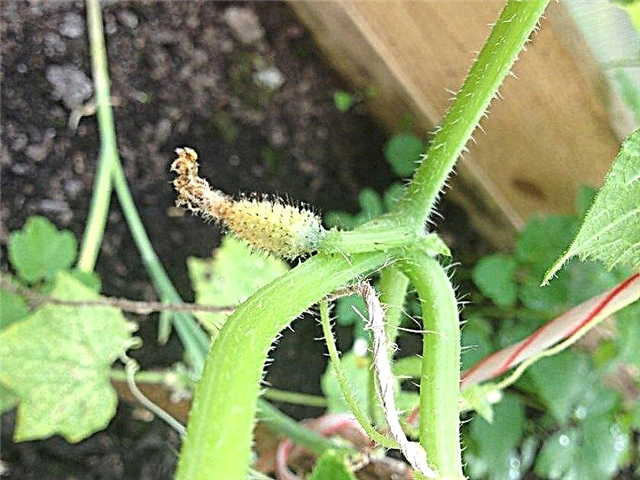

Pruning
The quality and quantity of the crop depends on the correct formation of the bushes. At the very initial stage of plant growth in the sinuses of the first 9-10 leaves, any “neoplasms” must be removed. Then, when the ovary begins to form, it should be normalized. On one bush there should not be more than 26–28 greens. This amount must be adhered to constantly.
Providing temperature
Optimum temperature conditions - + 15 ... + 25 ° С. Maintain this temperature range with a good ventilation system.
Important! It is very important that between “day” and “night” the temperature fluctuates between + 6 ... + 8 ° С.
Watering and feeding
Before flowering, the culture is irrigated once or twice a week through a watering can or drip irrigation system. On 1 m² you need to spend 4-5 liters of water. With the beginning of the flowering period and before the appearance of the first ovary, the frequency of irrigation increases and the volume of consumed water increases. On 1 m², pour 9–12 liters in 2-3 days. During the growth of the ovaries, the amount of water remains the same, and irrigation is done every other day.
For irrigation, you need to use only warm water with a temperature not lower than + 25 ° C. Irrigation procedures on hot days should be carried out early in the morning. If the weather is cloudy, then you can at lunchtime.
Nutrients are added weekly. Complex fertilizers for greenhouse crops are used. With prolonged adverse weather conditions (cloudy days in a row, a sharp drop in temperature), it is recommended to use supporting agents such as Epin-Extra or Zircon, as well as stimulants of the formation of ovaries.
Pollination
Without pollination, there will be no growth of the ovary, therefore, in order to attract insects to the greenhouse, you need to open it for ventilation when the weather is warm. In order for insects to fly better, the plant is sprayed with sweet syrup (1 liter of water, ½ tbsp. Honey or sugar) or use boron-magnesium fertilizers that can increase the production of nectar by flowers.
Prevention methods
In order for none of the described problems to interfere with growing a cucumber, one must resort to such preventive methods:
- Thoroughly prepare the soil before planting (fertilize, disinfect).
- To select and process seed.
- Plant plants strictly on schedule.
- Make timely formation and garter bushes.
- Weed and loosen the soil regularly.
- Regularly inspect the bushes for diseases and pests.
- Use only quality fertilizers.
- Dispose of any organic waste collected in the greenhouse in a timely manner.
- In the spring, treat the greenhouse with disinfectants.
- To treat young plants with fungicides and immunomodulators.
As you can see, all the causes of ovary yellowing are associated with the lack of proper attention to the culture. Therefore, you need not to be lazy and carefully care for the plant, observing all the rules and regulations.Did you know? The longest cucumber was able to grow Hungarians. Its length was 183 cm.